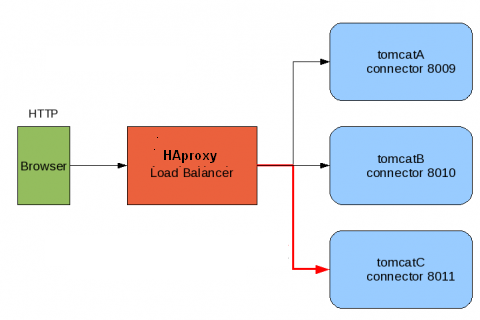
Multiple Tomcat Load Balancing on single VM with Highly-Available HAproxy
Apache Tomcat is an open source software implementation of the Java Servlet and JavaServer Pages technologies. The Java Servlet and JavaServer Pages specifications are developed under the Java Community Process. Apache Tomcat powers numerous large-scale, mission-critical web applications across a diverse range of industries and organizations.
We have lot of tomcat load balance method but this is simple method to load balance your tomcat application. Lets we discuss multiple Tomcat Load Balancing on single VM.
Important Tomcat Server ports
Connector Port : This is the port where Apache Tomcat listen for the HTTP requests.
Shutdown Port : This port is used when we try to shutdown the Apache Tomcat Server.
AJP (Apache JServ Protocol) Connector Port : The Apache JServ Protocol (AJP) is a binary protocol that can conduct inbound requests from a web server through to an application server that sits behind the web server.
Redirect Port : Any redirection happening inside Apache Tomcat will happen through this port. In Apache TOMCAT there are two instance where redirectPort is mentioned. First one is for the Apache TOMCAT server and other one is for the AJP port.
Do you want to load balance your multiple tomcat on single VM?
Download tomcat on your server different paths and extract it looks like the following folders (tomcat1 and tomcat2).
Tomcat uses a port (defaults to 8005) as a shutdown port. What this means is that to stop all webapps and stop Tomcat cleanly the shutdown scripts make a connection to this port and send the shutdown command.
The startup.sh and shutdown.sh script files make use of catalina.sh for performing the startup and shutdown operations. We shall edit catalina.sh it
Tomcat1
cd /usr/local/tomcat1/bin
vi catalina.sh
export CATALINA_HOME=/usr/local/tomcat1
export CATALINA_BASE= /usr/local/tomcat1
Tomcat2
cd /usr/local/tomcat2/bin
vi catalina.sh
export CATALINA_HOME=/usr/local/tomcat2
export CATALINA_BASE= /usr/local/tomcat2
You can optimize HTTP, HTTPS, AJP, Shutdown Ports for tomcat2. This will resolve tomcat ports conflict. open your server.xml and change ports.
vi conf/server.xml
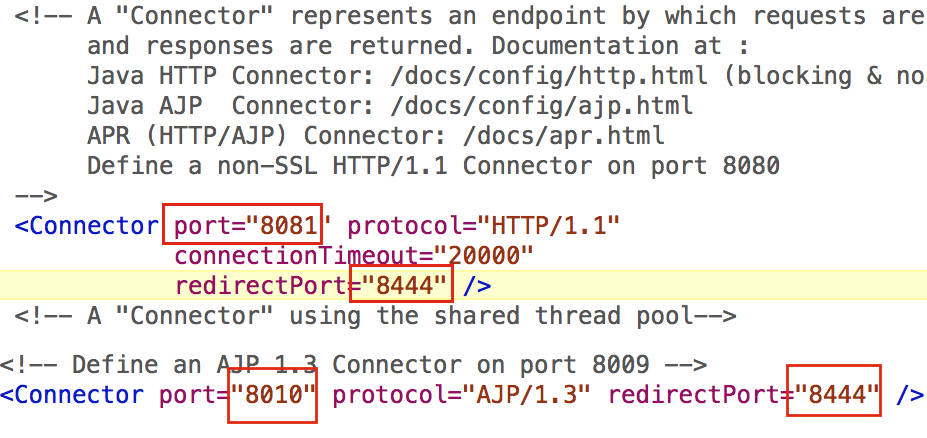
Thats all!!. You can start both tomcat and check with listen ports.
Start both tomcat1 and tomcat2.
#cd /usr/local/tomcat1/bin
# ./startup.sh
Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat1
Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat1
Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat1/temp
Using JRE_HOME: /usr
Using CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat1/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat1/bin/tomcat-juli.jar
Tomcat started.
Check tomcat listening properly.
# lsof -i tcp:8080
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
java 3830 root 42u IPv6 17199 0t0 TCP *:webcache (LISTEN)
# lsof -i tcp:8081
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
java 3059 root 42u IPv6 16143 0t0 TCP *:simplifymedia (LISTEN)
Install and Configure HAproxy loadbalancer
use this steps to install haproxy http://www.cloudkb.net/rabbitmq-cluster-setup-haproxy/
once the installation completed, open your haproxy configuration.
#vi /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Add below settings ( 192.168.1.133 is virtual public IP and 10.1.1.10 is local ip)
listen tomcat 192.168.1.133:8089
mode http
balance roundrobin
server tomcathost 10.1.1.10:8087 check inter 5s rise 2 fall 3
server tomcathost 10.1.1.10:8081 check inter 5s rise 2 fall 3
Restart haproxy
# /etc/init.d/haproxy restart
Stopping haproxy: [ OK ]
Starting haproxy: [ OK ]
Make sure your virtual port is open on firewall and browse now.
http://192.168.1.133:8089
This will display tomcat webapps/ROOT folder content.
In order to test load balance, you should shutdown tomcat1 or tomcat2 and check the content.
/usr/local/tomcat1/bin/shutdown.sh